When coupling with a structure such as Marc or Nastran, mesh deformation is required on CFD side
3 methods exist:
- Harmonic
- This method is useful for small deformation, cost is low. The Poisson equation is solved to propagate mesh deformation from the control point defined by the surface region
- This method is useful for small deformation, cost is low. The Poisson equation is solved to propagate mesh deformation from the control point defined by the surface region
- LDC
- This method suits quite well when deformation does not generate large deformation with High non-linearity
LDC determines the amount of movement from a certain node by the linear sum of the amount of movement specified by each surface movement condition.
The cost is lower than RBF and even faster.
The first step that initializes LDC method at the first iteration can be costly if the number of nodes is high
- This method suits quite well when deformation does not generate large deformation with High non-linearity
- RBF
- This method is very robust and can handle large deformation
It is a mesh-free method.
The cost is proportional to the square of the number of control points, in addition, memory consumption can be very High.
In mathematics, a radial basis function (RBF) is a real-valued function whose value depends only on the distance between the input and some fixed point
- This method is very robust and can handle large deformation
Picture below shows deformation field inside compuational domain depending on the method used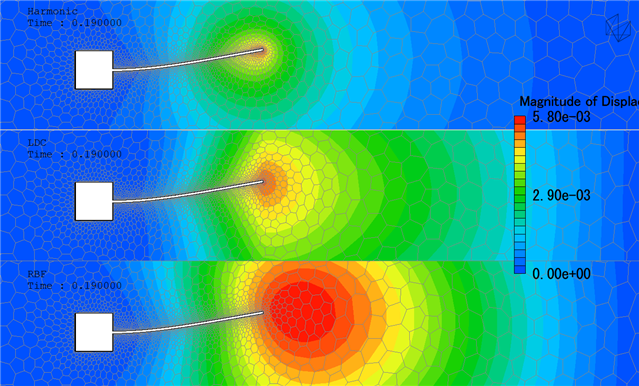
In addition to this mesh deformation, overset mesh could be required to handle contact between bodies such as a valve/membrane used in water pump for example
As described in the picture mesh deformation is applied only in the meshing unit that belong to the wetted surface
